Hello and welcome to the Salience local SEO cheat sheet! In this cheat sheet, we are going to give you everything you need to know to get started with local SEO, some best practices, and why local SEO is such an essential (yet overlooked) aspect of SEO.
What is Local SEO?
If you have ever searched for a local business such as a shop, office, and so on, you will have been subject to some local SEO.
Local SEO is the art of optimising for localised search queries, as these give unique results depending on location data.
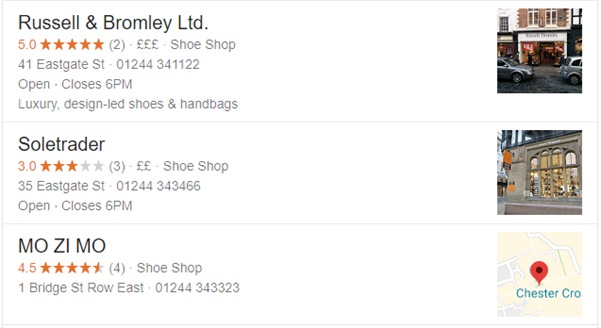
These queries will often come with a local business listing too:
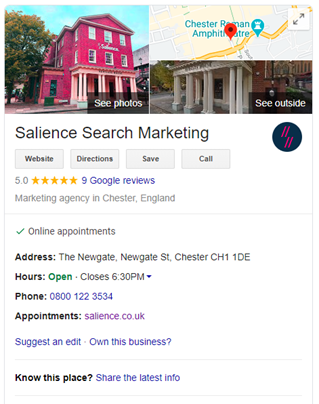
What is the difference between local SEO and traditional SEO?
As previously mentioned, local SEO will use location data to bring the most relevant search results for the user.
For example, if a user from Chester were to search for “Starbucks café”, they would expect to see a local, Chester result – rather than a search result for London!
This is where the local search result “snack packs” come into play:
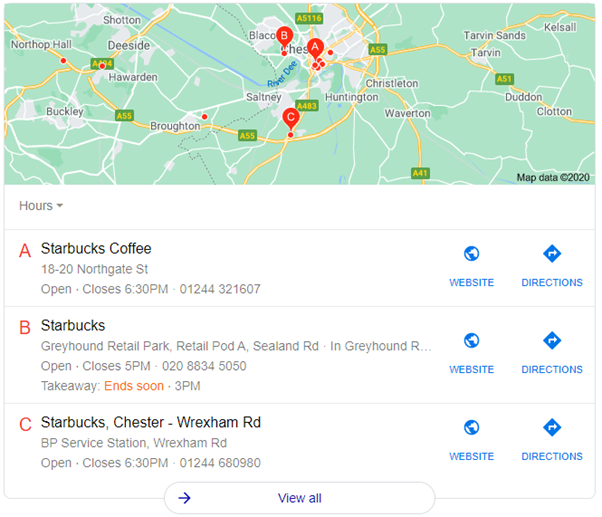
These are different to the normal search results and play a crucial role in serving the user intent – with one study stating that a third of clicks go to these local snack packs.
Why is Local SEO Important?
Because 46% of all searches have local intent – that is why!

And if that huge amount of potentially untapped traffic is not enough to convince you that local SEO is a huge market that needs to be targeted – Google themselves say 74% of consumers visit a store the same day that they search for something local on their phone!
How does Local SEO work?
It works in a very similar way that Google does, in which Google will scan its index and provide the best result to match the person’s query.
However, local SEO differs to traditional search as it has its own rules, guidelines, and ranking factors.
These ranking factors include:
- NAP citations
- Google My Business listings
- Searcher location
- Review sentiment
- Keywords on listings and in reviews
Plus, more. But we will revisit them later in the cheat sheet!
How long does Local SEO take?
As with all things SEO, it depends. It depends on the campaign, market, existing local SEO signals, and so forth.
However, in our experience, sites rank for competitive snack pack listings a lot quicker than they do for equally competitive keywords.
This may be due to fewer companies optimising for local SEO in comparison, but it is still a huge opportunity to gain some organic traffic and footfall!
How can I improve my Local SEO?
Google My Business Listings
Step one is to ensure you actually have a Google My Business listing! You can easily do this by simply searching your brand name. If your brand name is fairly new and might not be featured on Google yet, log in to your GMB profile or refine your search term.
If you need to register for an account, you can register here:
https://www.google.com/intl/en_uk/business/
Remove Duplicated Listings
Although these can happen accidentally, we recommend removing duplicate listings as soon as possible as these can dilute the rankings of the main listing.
To do this:
- Open Google Maps
- Find the location to report
- Click Suggest an edit
- Mark location as “Place is permanently closed or has never existed”
- Select “Duplicate” as the reason
- Submit
Update Listing with Correct Information
Having the correct information is critical to ranking well on local SEO. If you close at 6PM but your listing says 8PM, you are going to have some very unhappy potential customers if they turn up after your closing time!
Details we recommend ensuring are correct are as follows:
- Company name
- Opening and closing times
- Phone number
- Address
- Website
This applies to businesses with multiple locations too. The head office needs its own listing with information, and a store for example will also need its own individual information.
Extra Enhancements
Now that the framework is complete – we can look to start adding enhancements to further push the listing up the local SEO rankings!
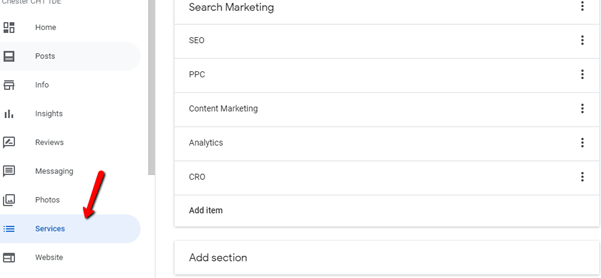
This involves adding primary and secondary business categories that best describe your business:
Be specific when choosing a category. For example, choose “Nail salon” instead of “Salon”. Use additional categories to let customers know more about the specific services you provide. If you manage a supermarket that includes a pharmacy and deli, you would choose “Supermarket” as your primary category and add “Pharmacy” and “Deli” as additional categories. – Google Guidelines
Update products and services:
Add a professional looking cover photo:
And finally, a short description of your business with keywords inserted where relevant.
Doing these steps will likely shoot you up the local SEO rankings, as well as helping you to stand out from the crowd by being more appealing to the eye – which should lead to a higher click through rate!
Reviews
Reviews are crucial to a successful presence online, as many users read reviews before purchase. This not only applies at a product level, but also on an organisational level. Review platforms such as TrustPilot are seeing more and more traction online – meaning having sufficient and good quality reviews is more important than ever.
Encourage Positive Reviews
Encouraging reviews is one of the best ways to gain reviews (shocker!), so long as the users’ expectations have been met. As generally, a happy customer won’t leave a review, this means that unprompted negative reviews are going to be more likely.
In terms of organic search, this is a huge red flag for Google, especially as positive sentiment is a part of Google’s algorithm.
Reviews do not need to be exclusively on Google platforms. External review platforms can be just as valuable. However, both should be considered, so sending a customer an email with a few options for them to choose from is a good idea.
Respond to Questions & Negative Reviews
Being active on your review platforms is a great signal to the user that you care about what they think.
On Google My Business, you may find that users will ask you questions. Anybody can reply to these; however, we recommend ensuring that the business owner answers them officially. Leaving these questions unanswered can be frustrating for users and may reflect negatively on the business.
The same goes for negative reviews. Replying to these show that you care and can often soften the blow for other users when reading the negative review.
There are right ways, and there are wrong ways to reply to negative reviews. We recommend reading this article for more information.
Onsite Changes
Onsite changes are some of the best ways to improve your local SEO. By making onsite changes, you can ensure that your website is corresponding with what is said on your GMB profile and making the user experience as positive as possible.
There are several ways onsite aspects can affect your local SEO:
Improve Page Speed
Page Speed is crucial to rank well on Google. This includes standard listings, PPC, and local. The quicker your website is, the quicker that users can find the answers they need.
Google also announced that Page Speed is a ranking factor.
Your website’s speed can be measured using Google’s PageSpeed insights tool. If you want to know how you can improve page speed, check out our post here.
Ensure Your Website is Mobile Friendly
Having a mobile-friendly website is a must in today’s web. Considering the majority of searchers are primarily mobile, and that now Google’s algorithm ranks “mobile-first” (the mobile version of a website), it is more important than ever.
If your website still is not mobile-friendly, we would recommend investing in a mobile responsive website as soon as possible. This will help you greatly in ranking on Google.
Cater Pages to Target Geolocation
Pages must be relevant to their respective geolocation, otherwise they are going to struggle to rank.
There is a myriad of different ways we can optimise for this, from page titles and meta descriptions to structured data. The important thing is that the information on the page is useful to the user without too much “fluff”.
External Changes
This is where it can become quite tough (although it can be incredibly rewarding!) to influence your local rankings. As a business ages, it will gain links called citations – these are generally created by an agency or the business itself.
Citations are essentially a record of your business details (phone number, address, website address, etc) that a user, or Google, can read.
In an ideal situation, all citations will be accurate and up to date. If not, it is worthwhile contacting webmasters with incorrect information and requesting them to update their details.
Local PR is also extremely valuable external content that can be generated, but this can be difficult to get!
In a nutshell, the more times we can get Google to see the details of your website, the better!
There we have it – a local SEO cheat sheet for you to digest and take away to implement. We hope that this guide was useful and if you have any questions or are unsure how you would go about implementing some of these changes – get in touch!
